Unveiling the workings of a GPU PCB: A Comprehensive Guide in 2024
Due to increasing demands for high-performance graphics and computing capabilities, greater awareness must be gained of various integral components within a computer system. One such part is the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) used within Graphic Processing Units (GPU). This article delves into all of its complexities by offering insight into its structure, core operations, practical implementations, technological developments in 2024 as well as potential avenues of technological growth.
Chapter 1: Understanding the Fundamentals – What Is a GPU PCB?
PCB stands for “Printed Circuit Board.” In computing terms, this physical structure forms the backbone of electronic devices, providing an assembly platform for critical components to assemble and interconnect. GPU PCBs include an array of components including Graphics Processing Unit itself, memory chips, power delivery systems, display outputs and any necessary auxiliary hardware…
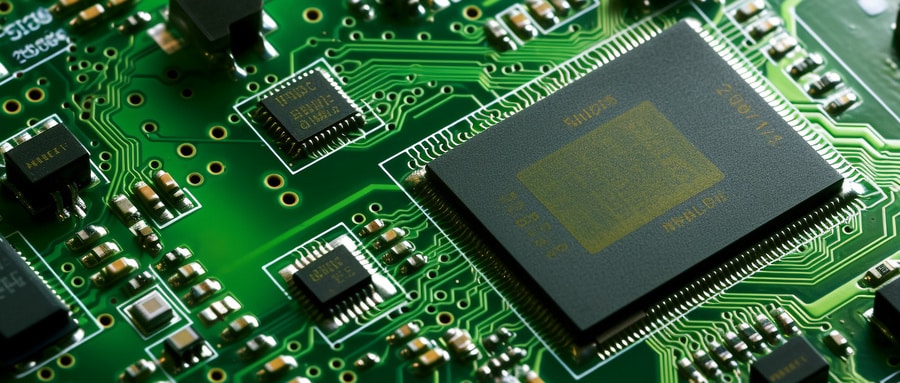
Chapter 2: GPU PCB Anatomy – Key Components
This chapter presents an in-depth examination of what makes up a GPU PCB, from GPU silicon and VRAM chipsets, Voltage Regulator Modules (VRMs), capacitors and inductors, all the way down to connectors – every part plays its own distinct part and working in concert together makes for a powerful combination. Understanding these units and their collective effect allows one to better appreciate just how powerful GPU really is…
Chapter 3: Exploring GPU PCB Functionality
Beyond physical construction, this section delves deep into how GPU PCB operates, including how electrical signals are transmitted, power delivery to various components, managing data between GPU and memory and understanding clock signals – just to name a few topics!
Chapter 4: Practical Implementations and Significance of GPU PCB
GPU PCBs have become an indispensable element of electronic devices, with applications spanning gaming computers and professional workstations to data centers and supercomputers. This chapter not only details current applications but also explores possible future ones in emerging technologies like AI, Machine Learning, Blockchain…
Chapter 5: Impact of PCB Design on GPU Performance
This segment examines how different PCB designs impact GPU’s performance. It examines why certain GPUs perform better in terms of performance, power consumption and thermal management due to specific PCB design strategies…
Gaining knowledge of the design, operation and functionality of a GPU PCB allows users to make educated choices when it comes to customizing their computing and gaming environments. This comprehensive guide seeks to equip readers with this knowledge as well as appreciate its latent potential; in an age driven by technological prowess such knowledge could prove vital in shaping future endeavors.
Dive into this comprehensive guide and gain access to the fascinating world of GPU PCBs today!
Note: This article will be regularly updated with current trends in GPU architecture and is intended as a reliable resource for both novice advocates and experienced technocrats. Stay tuned for more!
FAQ:
- Q: What is a GPU printed circuit board (PCB)?
A: A GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) printed circuit board is the board on which a GPU and its associated components are mounted. It facilitates the interconnection of these components and allows them to function as a cohesive unit. - Q: What components are typically found on a GPU printed circuit board?
A: A GPU printed circuit board typically includes the GPU itself, VRAM (Video Random Access Memory), voltage regulators, capacitors, resistors, a cooling solution, and various input/output (I/O) connectors. - Q: What materials are commonly used in a GPU printed circuit board?
A: Like other PCBs, GPU printed circuit boards consist of thin layers of conductive and non-conductive materials. The core of the PCB is typically made from FR4, a type of fiberglass. Copper traces are created on these layers to allow electrical signals to flow between components. - Q: How does a GPU printed circuit board contribute to the performance of a GPU?
A: The layout of a GPU printed circuit board can influence the GPU’s performance. Efficient routing of electrical traces, effective cooling solutions, and quality power delivery circuits can all contribute to optimal GPU performance. - Q: How does cooling impact the design of a GPU printed circuit board?
A: Cooling is crucial for a GPU’s operation. Appropriate spacing is required on the PCB for heat sinks, fans, or liquid cooling solutions. The PCB may also include temperature sensors to monitor thermal performance. - Q: How do you clean a GPU printed circuit board?
A: GPU PCBs can be cleaned using compressed air, isopropyl alcohol, and anti-static cloths. However, it’s vital to ensure the board is completely dry before reinstalling it to prevent electrical shorts. - Q: Can a damaged GPU printed circuit board be repaired?
A: Some damage to the GPU printed circuit board, such as a broken trace or a blown capacitor, may be repairable. However, due to the small scale at which these boards operate, professional expertise is usually required. - Q: Can I customize the PCB of my GPU?
A: While customization can be difficult due to the complexity of GPU printed circuit boards, enthusiasts may modify certain aspects like cooling solutions or perform hardware modifications called “hardmods”. - Q: Why do GPU printed circuit boards often have a black or green color?
A: The color of a PCB is determined by the solder mask that covers much of the board’s surface. While green is traditionally used due to its heat resistant properties and cost-effectiveness, black or other colors can also be used for aesthetic reasons. - Q: What care or precautions should be taken with a GPU’s PCB?
A: Due to the sensitive nature of PCBs, it is essential to avoid handling them with bare hands to prevent static electricity buildup. Also, ensure proper cooling measures to prevent high temperatures, which can damage the components.























